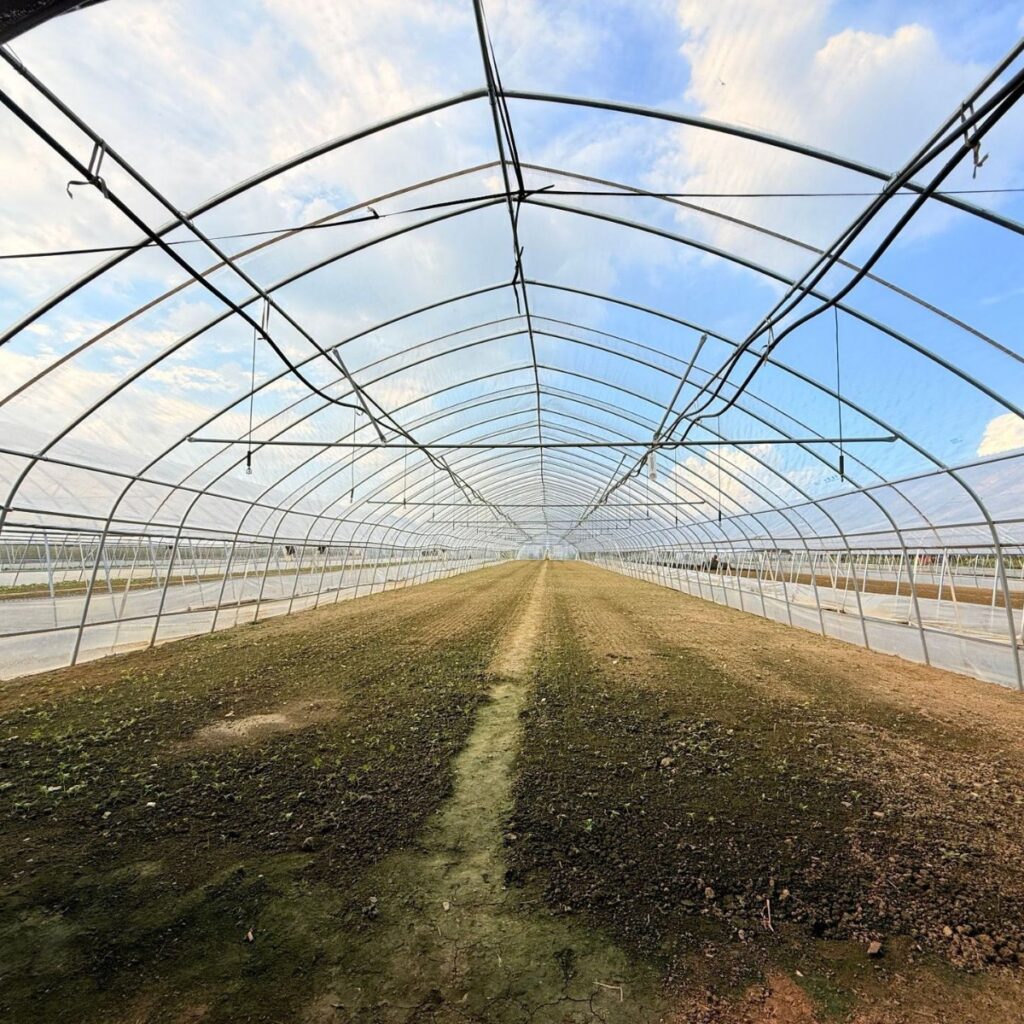
For many home gardeners, building a green house is a step toward more freedom in planting. It’s not only about keeping plants safe from the weather, but also about creating a space where you can experiment, grow out of season, and try crops that wouldn’t survive in your backyard otherwise. Before buying or setting one up, it’s worth looking at the options for green house material, the right size, and a few extras that make gardening inside a greenhouse more effective.

Choosing Between Plastic and Glass
The first decision most gardeners face is the covering. Green house plastics are often the go-to choice for hobby growers. They’re inexpensive, light to handle, and modern polycarbonate panels provide decent insulation while letting in plenty of sunlight. If you want something easy to manage and budget-friendly, this is usually the way to go.
A glass green house, however, has a timeless appeal. Glass offers clarity and allows maximum light to reach your plants, which is a big advantage in cooler or cloudier regions. It’s heavier and more expensive, but it lasts for decades if maintained well. Many people who prefer glass choose glass green house kits, which take away the guesswork by including pre-cut panels and a compatible frame.

Why the Frame Matters
No matter which covering you choose, the structure holding it up is critical. A green house frame kit is a popular option because it gives you all the pieces you need, often in aluminum or galvanized steel. These metals are resistant to rust and can handle strong winds better than makeshift wooden frames. It’s one of those areas where investing in quality pays off—you don’t want to be patching up your greenhouse every storm season.
Heating and Climate Control
Temperature is another factor that can’t be ignored. When winter comes, a green house heater makes the difference between plants thriving or freezing. Even a small portable heater with a thermostat can keep temperatures stable enough for seedlings or tender crops. Ventilation is just as important; without it, humidity builds up, and diseases spread quickly. A balance of heating, airflow, and insulation creates the ideal growing environment for most green house plants.
How Big Is an Average Green House?
A question many beginners ask is: how big is an average green house? There isn’t one exact answer, but for most home gardens, a structure between 6×8 and 8×10 feet works well. It’s large enough to hold shelving and raised beds but not so big that it becomes expensive to heat or maintain. Larger sizes, such as 12×20 feet, are often chosen by growers who want to produce food on a bigger scale or experiment with more plant varieties.
What to Grow Inside
One of the joys of greenhouse gardening is that you’re not limited to your local climate. Common choices for green house plants include tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and leafy greens. Herbs like basil, rosemary, and parsley do especially well in pots on shelves. Some gardeners even use the stable environment to grow orchids or other tropical flowers that would never survive outdoors in colder regions.
Getting Started with Kits
For anyone new to greenhouse gardening, kits simplify the process. Both glass green house kits and green house frame kits usually come with everything you need for assembly, including instructions. They’re designed so even someone with little building experience can set up a functional space in a weekend. It’s a practical way to start without the stress of sourcing each piece separately.
Final Thoughts
Whether you prefer the affordability of green house plastics or the elegance of glass, setting up a greenhouse is an investment that pays back in fresh produce, healthier plants, and year-round gardening opportunities. Add a heater for the cold months, choose a frame that can stand up to your climate, and decide on a size that fits your goals. With those elements in place, your greenhouse will become more than just a structure—it will be a space where gardening never really ends.
Green House FAQs:
How big is an average green house?
The average green house size can range from 6×8 ft for small backyards to over 10×20 ft for larger gardens. The right size depends on how much space you have and the type of plants you want to grow.
What is the best green house material?
Common green house materials include aluminum frames, wood, and steel. For coverings, many buyers choose green house plastics (polycarbonate or polyethylene) for affordability and insulation, while a glass green house provides excellent light transmission and durability.
Do I need a green house heater?
If you live in a cold climate or want to grow plants year-round, a green house heater is recommended. It helps maintain stable temperatures, especially for tropical plants or during winter.
Which is better: green house plastics or glass green house?
Both have benefits. Green house plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and good at heat retention. A glass green house offers a classic look, high light clarity, and long-term durability, though it may cost more.
Are green houses eco-friendly?
Modern green house materials are often recyclable, and using efficient heaters or solar-powered systems can reduce environmental impact.





